
Kerberos Attack: Threats and Defences
In cybersecurity, attackers continuously strive to exploit vulnerabilities and weaknesses within systems and protocols. One such attack that has gained notoriety is the Kerberos attack. Kerberos, a widely used authentication protocol, is designed to provide secure access to network resources. However, like any technology, it is not immune to exploitation. This article delves into the intricacies of the Kerberos attack, shedding light on its mechanisms, potential consequences, and strategies to defend against it.
Kerberos Authentication
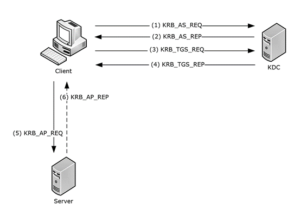
Kerberos is a trusted third-party authentication protocol developed by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). It uses a ticket-based system to provide secure authentication in network environments, allowing users to access resources without constantly transmitting passwords over the network. The Kerberos protocol relies on a Key Distribution Center (KDC) and the exchange of encrypted tickets to validate users’ identities.
Types of Kerberos Attacks
- Kerberos Spoofing: Attackers attempt to impersonate legitimate users by intercepting and manipulating Kerberos tickets. They may obtain Ticket Granting Tickets (TGTs) and use them to gain unauthorized access to network resources.
- Kerberos Ticket Replay: Attackers capture legitimate tickets exchanged between clients and servers, then replay these captured tickets to gain access to resources without needing to authenticate.
- Golden Ticket Attack: Infiltrators create forged TGTs with arbitrary privileges, effectively granting themselves unrestricted access to a network. This attack often involves compromising the Key Distribution Center (KDC) or obtaining its cryptographic keys.
- Silver Ticket Attack: Attackers exploit vulnerabilities to forge service tickets for specific services, thereby gaining unauthorized access to those services with potentially escalated privileges.
- Pass-the-Ticket Attack: This attack involves using captured service tickets (TGS tickets) to impersonate a legitimate user and access specific services, even without knowing the user’s password.
Impacts of Kerberos Attacks
Kerberos attacks can have severe consequences, including:
- Unauthorized Access: Attackers can gain unauthorized access to network resources, potentially compromising sensitive data and systems.
- Data Breaches: If attackers successfully gain access to a network, they may exfiltrate sensitive data, resulting in data breaches and potential legal and reputational damages.
- Disruption of Services: By impersonating authorized users or administrators, attackers may disrupt services, causing downtime and financial losses.
Defending Against Kerberos Attacks
- Regular Patching: Keep all systems and applications up to date to address known vulnerabilities that attackers might exploit.
- Least Privilege Principle: Limit users’ access to resources based on their job roles. This reduces the potential impact of an attack.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate critical systems and sensitive data on separate network segments to minimize the spread of an attack.
- Strong Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security beyond passwords.
- Monitoring and Detection: Utilize intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) tools to detect anomalous behavior and potential attacks.
- Privileged Access Management: Control and monitor privileged accounts closely to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive systems.
Conclusion
The Kerberos attack highlights the importance of vigilance and robust security measures in the digital age. As organizations rely on authentication protocols like Kerberos to secure their networks, attackers continually seek to exploit vulnerabilities within these systems. By understanding the mechanics of Kerberos attacks and implementing proactive security practices, individuals and organizations can better defend against potential threats, safeguard sensitive information, and maintain the integrity of their network environments.
